Marketing Data Analytics for Reporting: The Essentials
Analysis is that process of finding things out — of looking for meaning within your data. Analytics uses computers for data analysis, making it much faster and more effective.
That all sounds great. But what does it mean for marketers?
A lot, actually! Data analytics has revolutionized marketing, and it’s part of what makes digital marketing so powerful. If you don’t know which tools to use to analyze your marketing data, here’s a guide to the best apps for marketing reporting.
Today, we’ll give you an introduction to everything you need to know about marketing data in the digital age.
What are marketing data analytics?
In a marketing context, ‘analytics’ usually means analyzing data on customers, and the campaigns and content you’ve created to reach them.
Data and analytics let marketers base their strategy on evidence. It’s all about knowing exactly how your tactics perform, so you can double down on what’s working, and scale back on what’s not.
With analytics, marketers don’t need to guess what their customers want, or what strategy will get them the best results. They can see exactly how their campaigns are performing, improve them as needed, and create better outcomes for their company. These tools use data integration to centralize information from multiple sources.
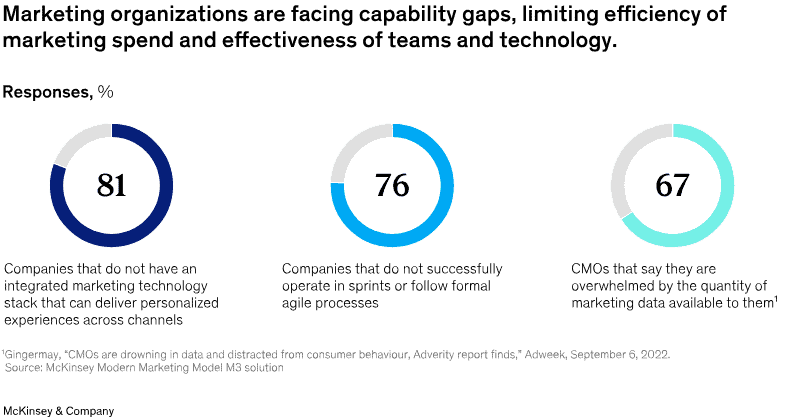
Marketing analytics 101: Using the right metrics
Marketers use many different metrics to track if they’re reaching their goals.
Here are a few of the most important metrics across general marketing, email, social media, paid ads, and SEO.
Return on investment (ROI)
This is a general metric to describe how much profit your marketing activities are generating, compared to what they cost. Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) is a common way to measure ROI from paid search or social media ads.
Customer lifetime value (CLV)
This metric tracks how much income each customer will create over the course of their customer journey. This is a useful way to measure ROI. By calculating the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer throughout their relationship with the company, CLV provides a long-term perspective on the profitability of marketing strategies.
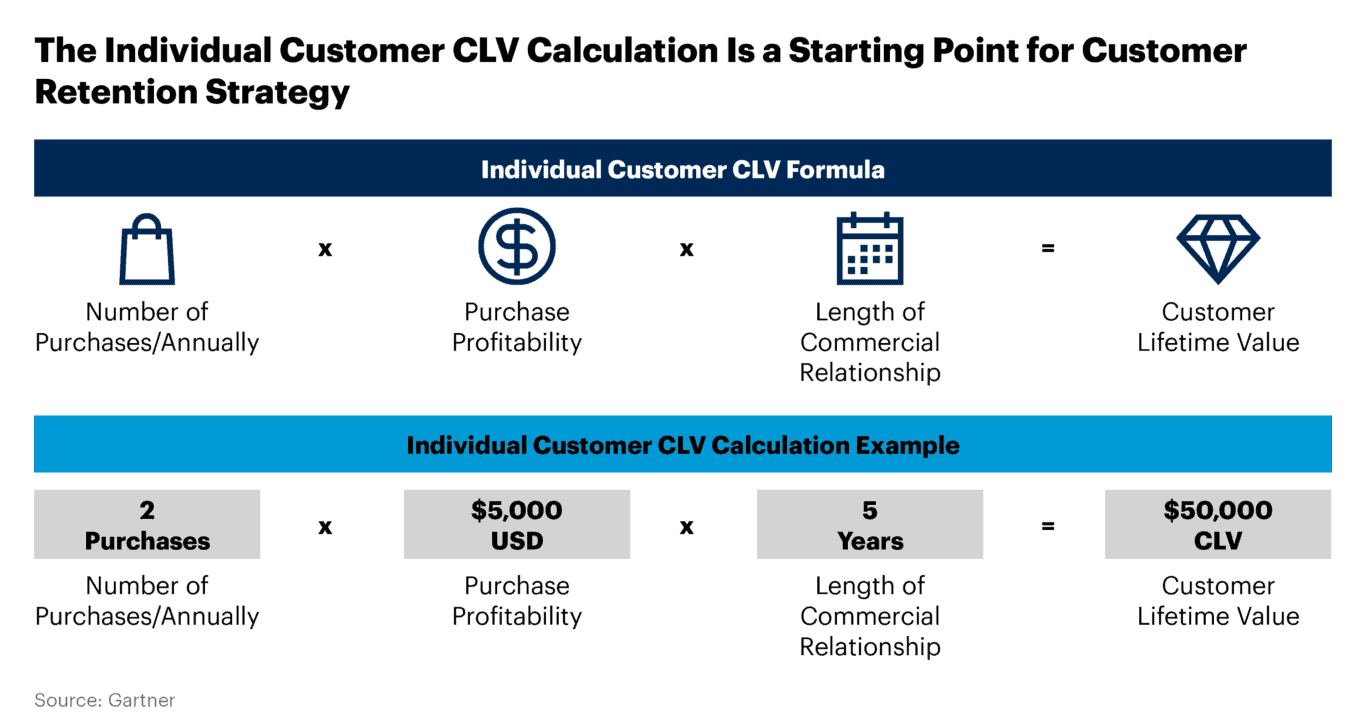
This metric essentially contrasts the costs of acquiring and retaining a customer with the total revenue generated from them over time. Using CLV as a measure of ROI simplifies the evaluation process, enabling marketers to clearly see whether the investments in attracting and maintaining customers are yielding profitable, sustainable relationships.
This makes CLV not just a metric for immediate campaign performance, but a strategic tool for assessing the overall health and effectiveness of a company’s marketing approach over time.
From Gartner:
Customer lifetime value (CLV) vs. Lifetime value (LTV): What’s the difference?
Often used interchangeably, lifetime value (LTV) and customer lifetime value (CLV) have a key difference. LTV looks at the aggregate value of all customers, while CLV focuses on each customer’s worth to the business.
Calculating CLV gives you a holistic view of a customer’s history with your company and pinpoints those most likely to buy from you again. LTV, in contrast, provides a more general view of your overall customer base.
Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
A measure of how much money a company must invest to gain each new customer, and another way of measuring ROI. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a vital metric for calculating the Return on Investment (ROI) of marketing efforts.
Essentially, CAC measures the total cost associated with acquiring a new customer, which includes all marketing and sales expenses over a specific period divided by the number of customers acquired during that period.
How to assess ROI using CAC
Businesses cam compare the cost of acquiring customers (CAC) against the value those customers bring (often measured in terms of revenue or Customer Lifetime Value – CLV).
A lower CAC relative to the high customer value signifies a strong ROI, indicating that the marketing efforts are efficient and effective in generating profitable customer relationships.
Conversely, a high CAC compared to customer value suggests that marketing strategies may be less efficient or sustainable in the long run.
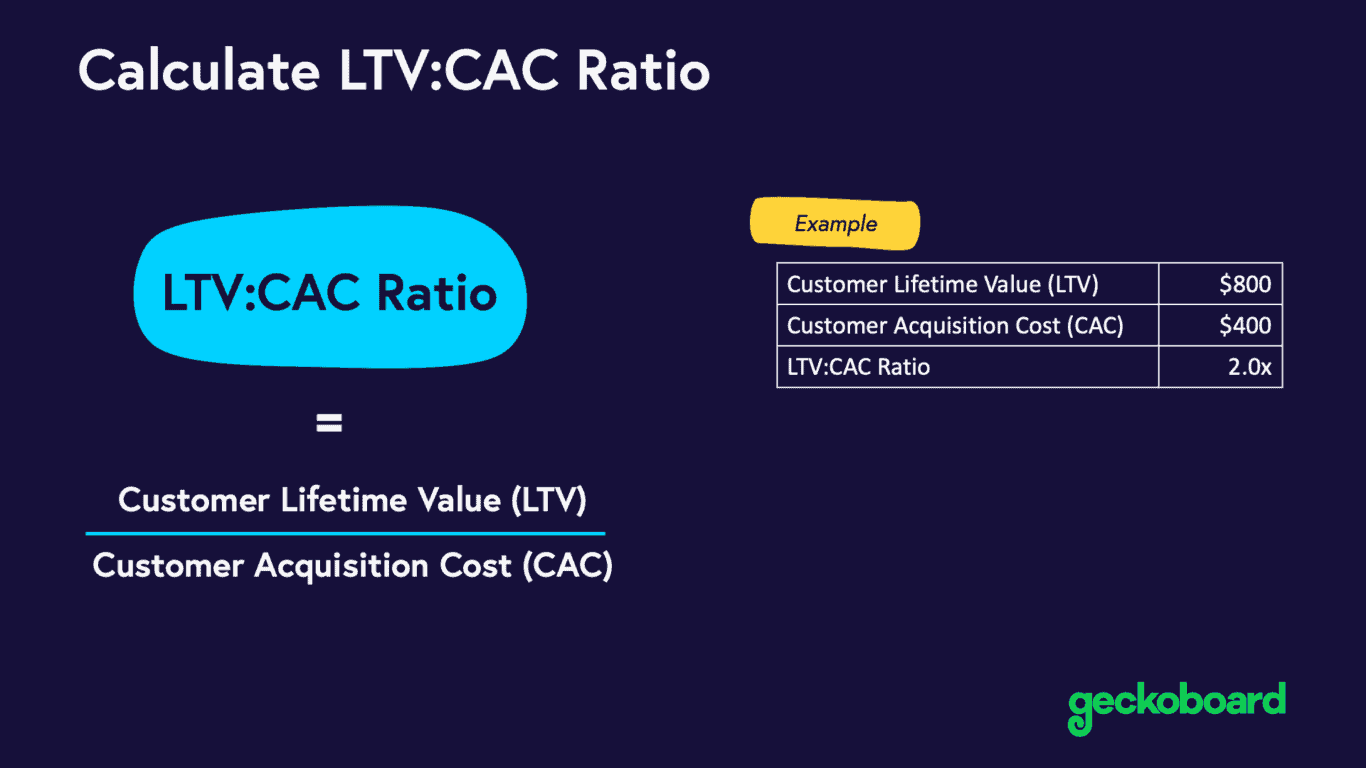
Therefore, by analyzing CAC, businesses gain essential insights into the direct financial impact of their marketing strategies, allowing them to make informed decisions about how to optimize their marketing spend for maximum ROI.
Conversion rate
This marketing analytics metric measures which percentage of your customers, or potential customers, are taking a specific action, such as making a purchase. Click-Through Rate (CTR) is a type of conversion rate often used in email marketing
Engagement and reach
These social media marketing metrics are an essential part of marketing analytics. Reach tracks how many users saw your social content while engagement describes how many users interacted with your content, such as through comments and shares.

Search traffic and keyword ranking
Also known as SEO, Search Engine Optimization marketing metrics are useful for creating content that gets better traction in search engines. Search traffic measures how many users are being driven to your site from search engines while keyword ranking describes how close to the top of search results your content appears.
The importance of marketing analytics
Marketing data is important because it’s proof that your strategy is working — or not.
In the Mad Men days of yesteryear, marketers might release an entire ad campaign and not know how it performed until months later, when they reviewed annual or quarterly sales. Even then, they wouldn’t be able to say for sure how the campaign contributed to those results.
Today, things couldn’t be more different. Because most marketing now happens online, it generates a high volume of data. You don’t have to guess how many people saw your campaigns, or if those impressions led to valuable actions like purchases — you have near-instant data to know for sure.
That lets marketers work in a highly informed, responsive way. Data lets you constantly iterate and improve, generating better returns not just financially, but also on the hard work and creativity you put into what you do.
How to use marketing analytics
But what does data-driven marketing actually look like in a practical context?
Here’s an example data-driven workflow, for a few different types of digital marketing.
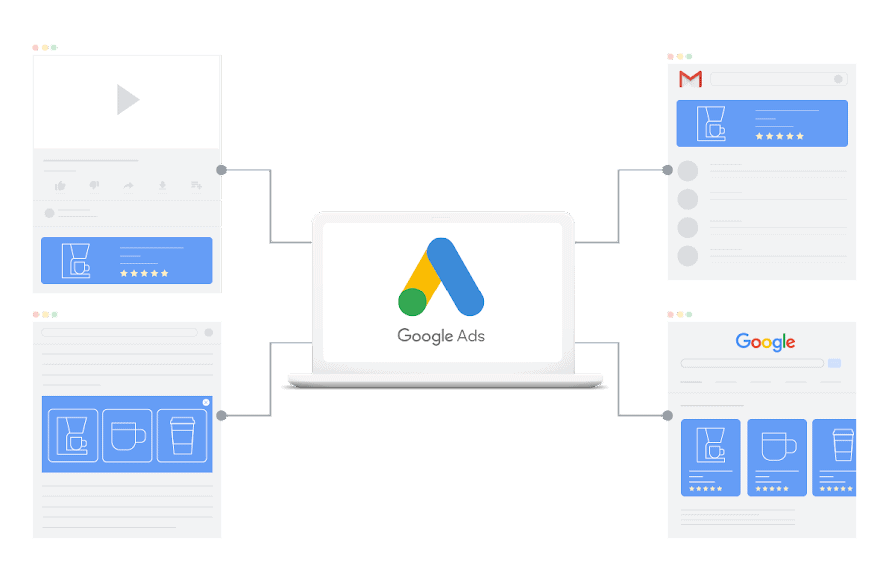
Paid social media or search engine ads
- Design two ads for the same product, but with different content
- Run both through Google Ads, Facebook Ads Manager, or another platform
- A/B test the two ads and analyze which performed better
- Replace the lower-performing ad, then keep repeating the process
Organic SEO
- Use a keyword research tool to identify popular, relevant keywords with low competition
- Publish original content targeting the keywords
- Analyze how much traffic that content brought to your website, and how highly it ranks for its keyword
Organic social media
- Create regular reports on your social media content’s performance. Track metrics like reach, likes, and comments on each post
- You can also track how many conversions your content prompted, like newsletter signups or the use of a discount code
- In the future, emphasize the kind of content that performs best with your audience
Email marketing
- Most email automation tools offer built-in analytics
- Email marketers can take an A/B testing approach similar to paid ads, or a reporting-based approach like a social media marketer would
Top marketing data and analytics software
It’s never been easier for marketers to bring data into their process. From free beginner options to super-advanced, powerful solutions, there are now analytics software tools for nearly every type of marketing.
Here are the most important types of data analytics tools for marketing, and a few of the most popular options in each category.
Customer relationship management systems (CRMs)
These all-in-one systems track many kinds of customer data, across marketing, sales, and customer service.
CRMs aren’t exclusively for marketing, but they contain plenty of information that’s valuable to marketers.
Top CRMS:
Paid social media and SEO
This type of marketing is inherently data-driven. Marketers can buy, publish, and analyze pay-per-click (PPC) and other types of paid ads all within one platform.
Social media ads can also often be analyzed with social media analytics tools, which we’ll cover next.
Top paid ad tools
Unito now supports integrations for Google Ads and GA4
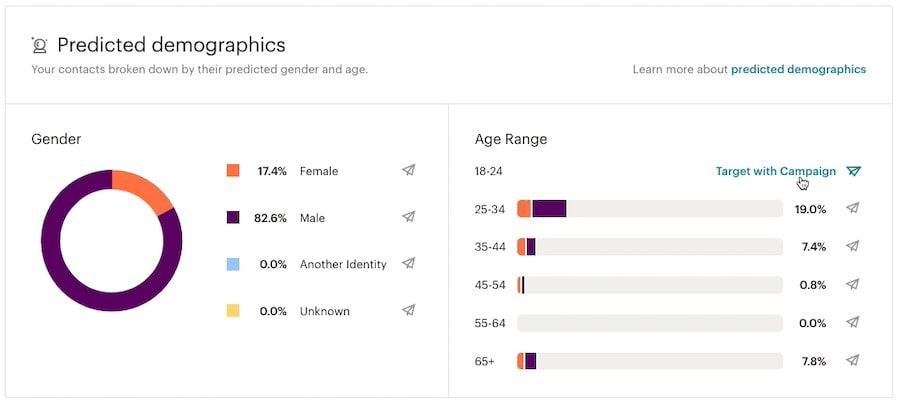
Social media marketing analytics tools
There are many great software tools for social media marketers.
Most of these tools allow users to plan and schedule their posts, as well as analyze their performance.
Top social media analytics tools
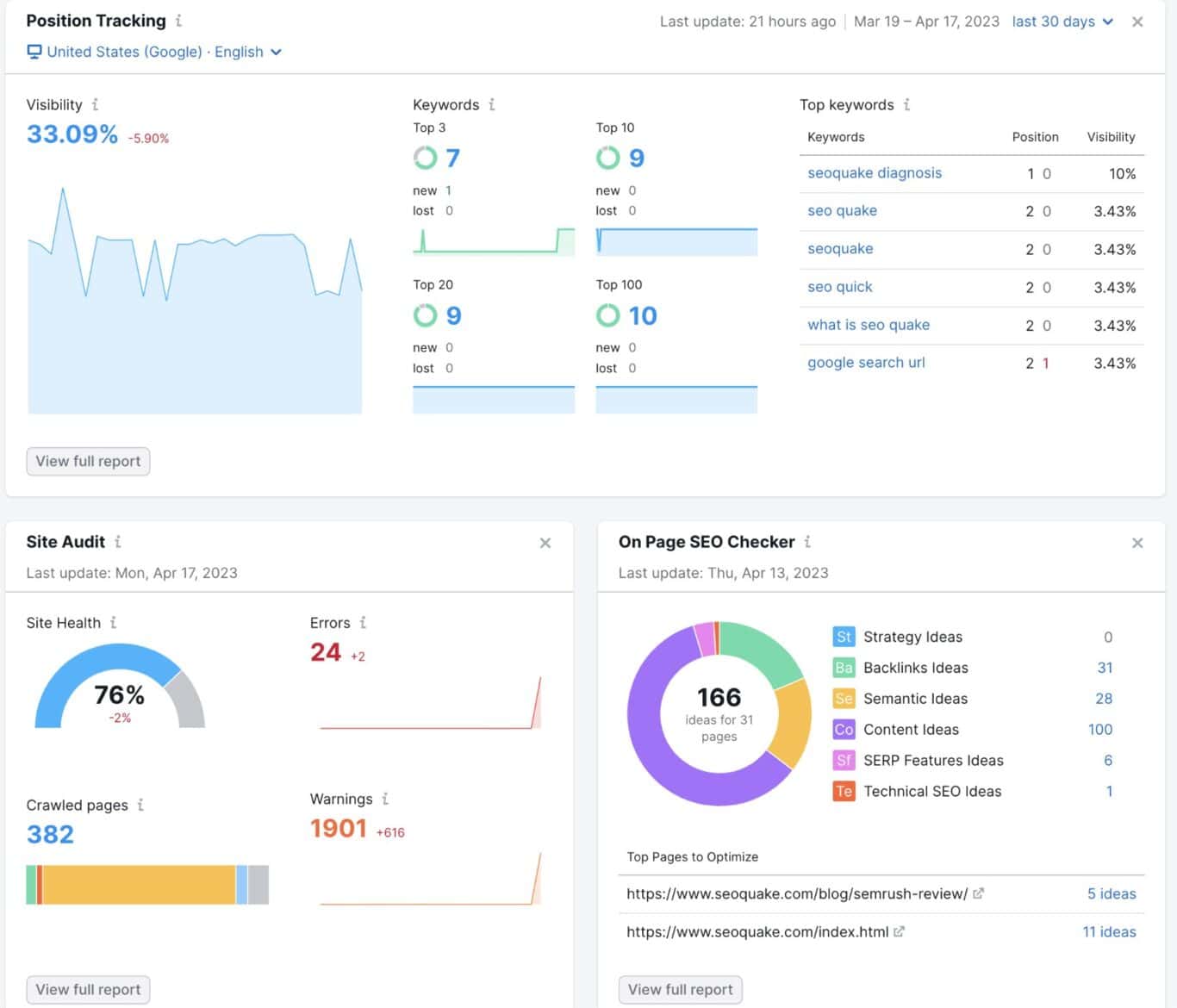
Organic SEO analytics tools
SEO marketers can use data at every step of their process. Here are some of the most popular tools to research keywords, optimize content, and analyze performance.
Top SEO tools
- SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz for keyword research and analysis
- Clearscope to analyze and optimize written content
- Google Search Console for understanding keyword ranking
- Google Analytics for analyzing search data, visitor insights, trends, and other website traffic

Here’s our guide to creating an effective marketing dashboard in Google Analytics 4 (GA4).
Email marketing analytics and automation tools
Email marketing tools don’t just offer analytics — they streamline marketers’ whole process.
Most email software, particularly for marketing reporting, lets users create segmented audiences, send mass emails to thousands of customers at once, and track important metrics like open and click-through rates.
Did you know Pipedrive and Mailchimp are both supported by Unito? Here’s how to handle lead lifecycle management with both tools:
Top email analytics tools
Marketers love data
In the 21st century, marketers are lucky! We have access to a wealth of data to help us reach our customers, make good decisions, and deliver amazing results.
Creativity still matters — it’s how you create fresh, beautiful content that surprises and delights your customers.
But data helps us understand how customers react to that creativity, and keep reworking our ideas around their needs, preferences, and values.