How To Set up a GitHub-Jira Integration (2 Methods)
Maybe your developers are sick of copying and pasting their updates from GitHub to Jira. Or maybe product managers, team leads, and other stakeholders have no idea what’s going on in GitHub and are struggling to properly steer your projects. No matter what initially sparked the need, you have to find a GitHub integration for Jira that’ll work without breaking the bank. So what do you do?
Read on to learn about the two most popular methods for setting this up. Or you can follow our detailed guide on how to quickly sync issues between GitHub and Jira with Unito.
First method: Use the built-in GitHub to Jira integration
Did you know that Atlassian offers a free app for setting up a GitHub integration with Jira? With a few clicks and some configuration, you can quickly start integrating updates from GitHub into your Jira issues, giving PMs and team leads a way to check in on development work without having to dive into a GitHub repository.
Here’s how you can set this up.
Install the app
Start by going to the Atlassian marketplace, where you can find a ton of apps that can help you tailor your Jira projects to your needs. You’ll find the GitHub for Jira app here, or by searching up “GitHub for Jira” on the marketplace.
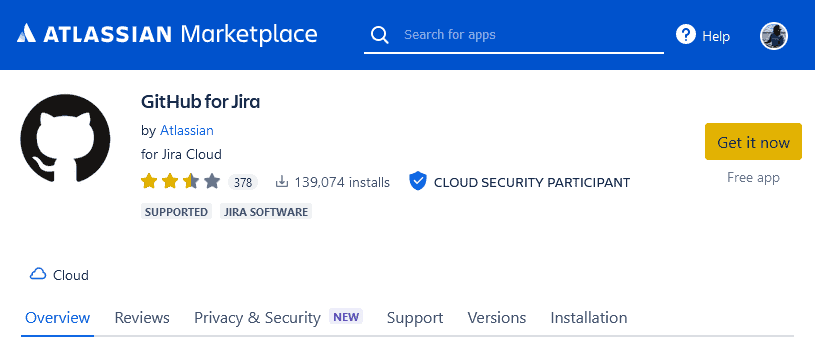
From there, just hit Get it now to start adding it to your Jira workspace. If you’re not logged in to Jira, you may need to log in, and then pick the Jira project you want to add the app to. Otherwise, you’ll be taken to your Jira workspace where you’ll see this screen. Hit Get it now.
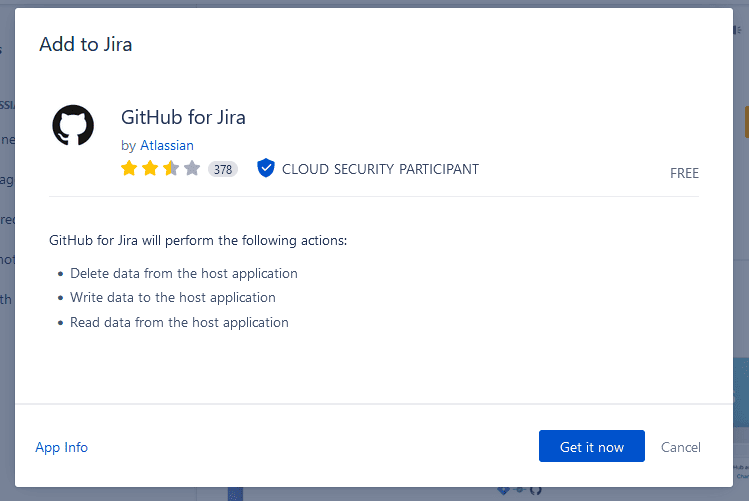
It should only take a few moments for the app to be added to your Jira workspace.
Setting up your GitHub integration with Jira
Now that the GitHub for Jira app is added to your workspace, it’s time to connect it to your GitHub repository. You should see this screen.
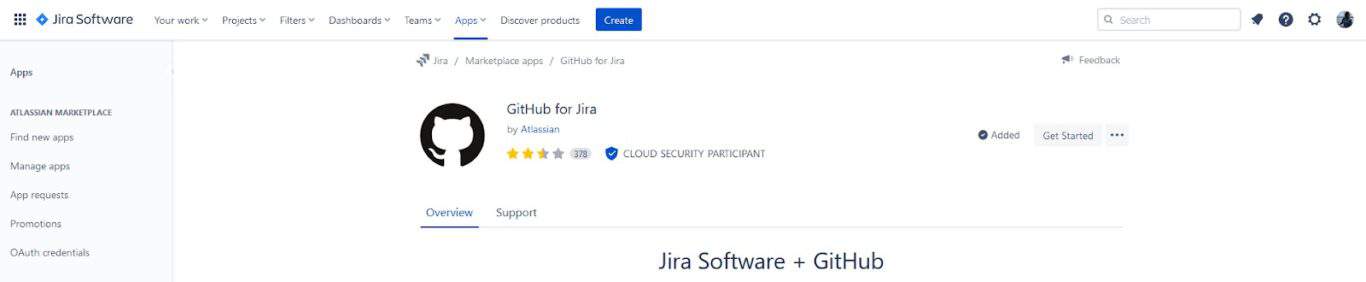
Hit Get Started.
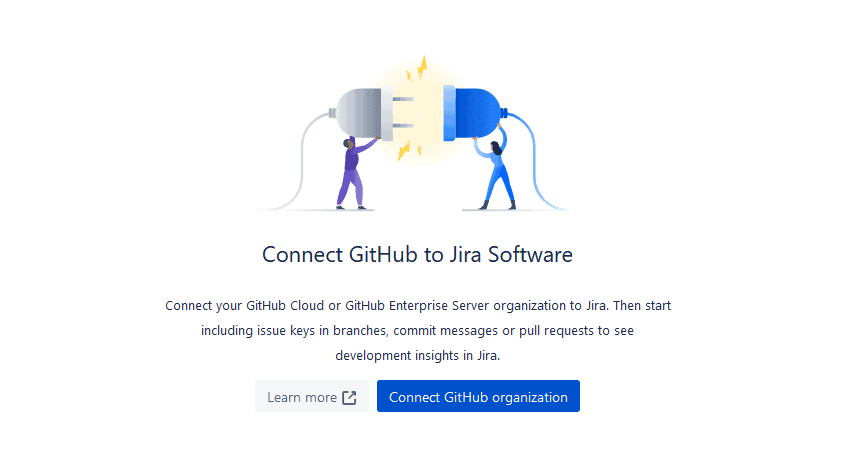
After that, hit Connect GitHub organization.
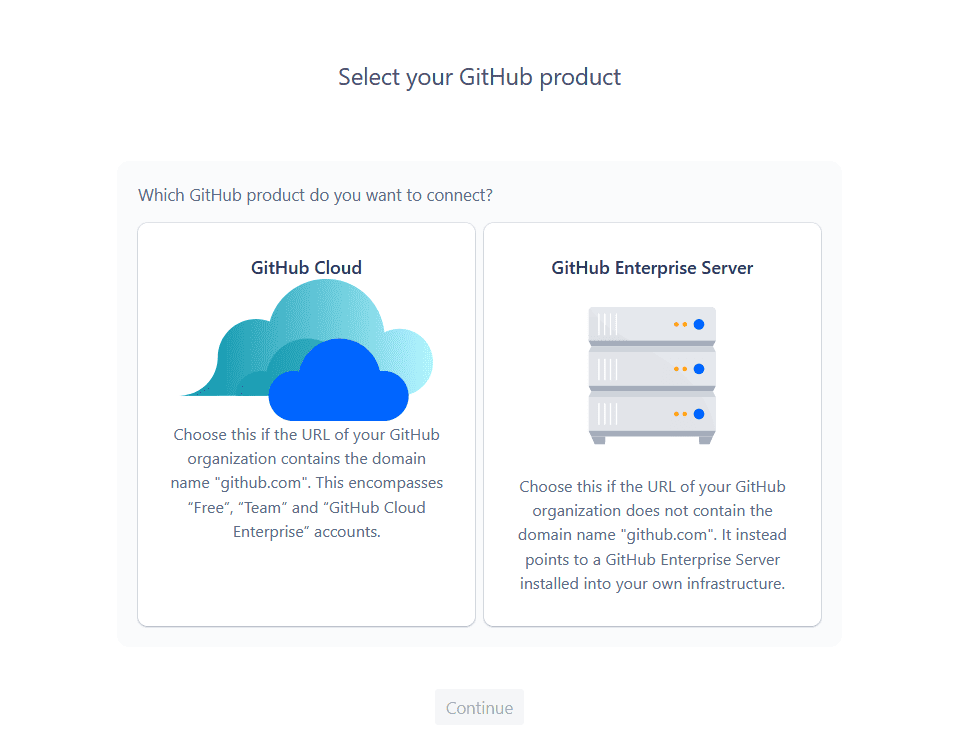
Here, choose whether you’re connecting a repository from GitHub Cloud or GitHub Server. If you’re not sure what you need to connect, get in touch with IT or a system administrator. After you’ve picked the right option, hit Continue. You’ll then get this screen.
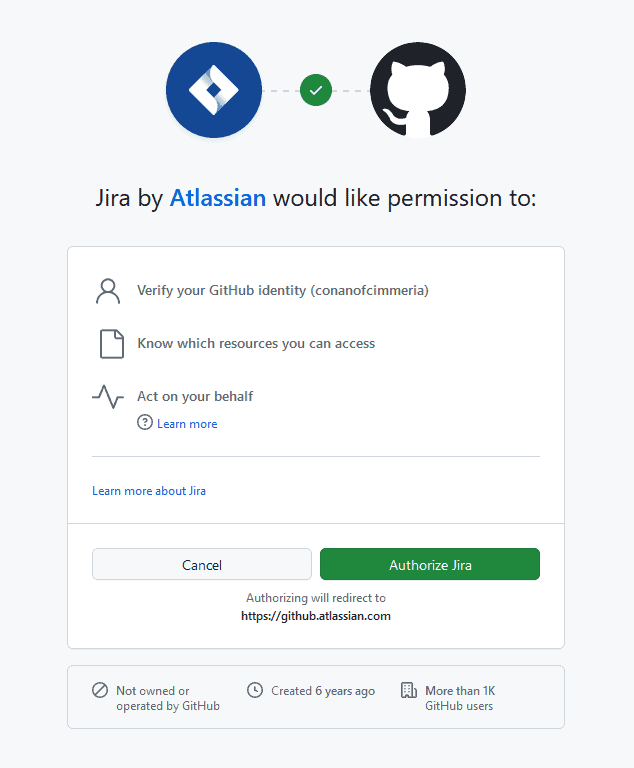
This lists the permissions that Jira needs from your GitHub account to properly sync issues across tools. If you’re not sure what you’re looking at, get in touch with IT or an administrator before you hit Authorize Jira. Once that’s done, you’ll see this.
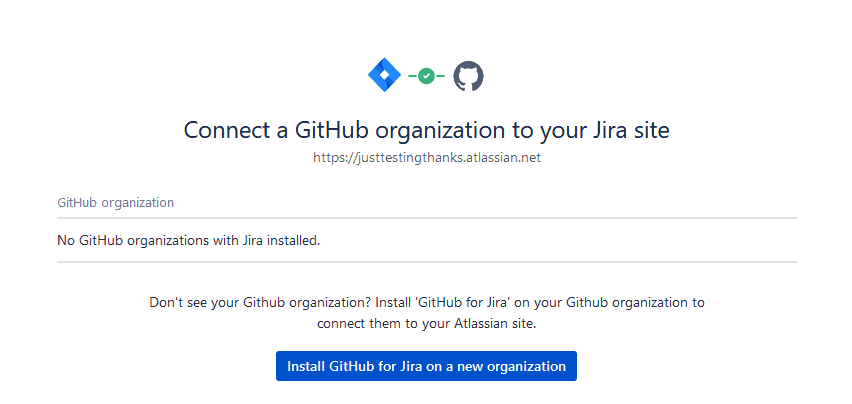
That’s because there’s still a bit of setup to do on the GitHub side. Start by hitting Install GitHub for Jira on a new organization.
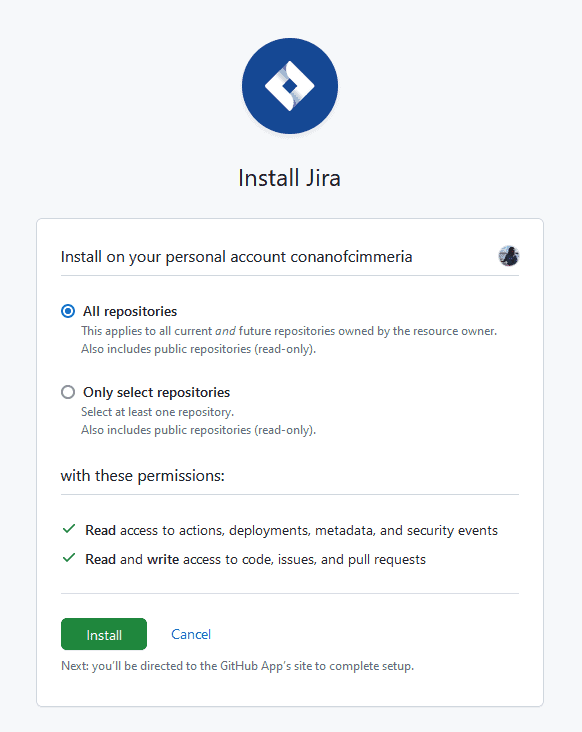
At this stage, you’ll be adding a Jira connection to the GitHub repositories you want to sync. You can choose to connect all repositories associated with your GitHub, or only a select few. Once you’ve chosen the repositories you want to connect, just hit Install, following which you’ll see this.
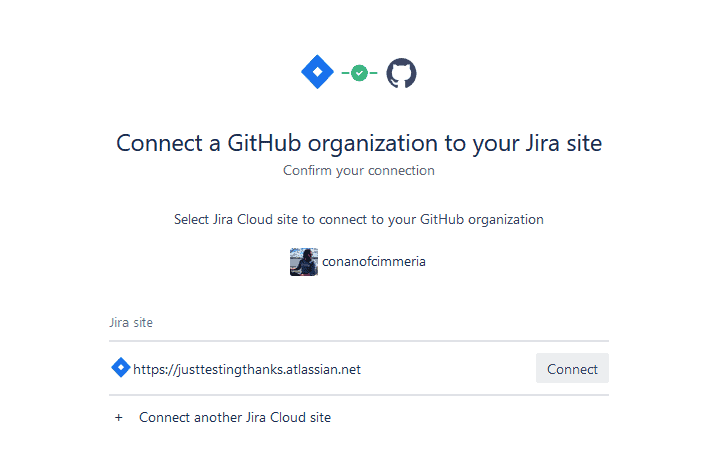
Now hit Connect on the Jira site you want to sync with GitHub.
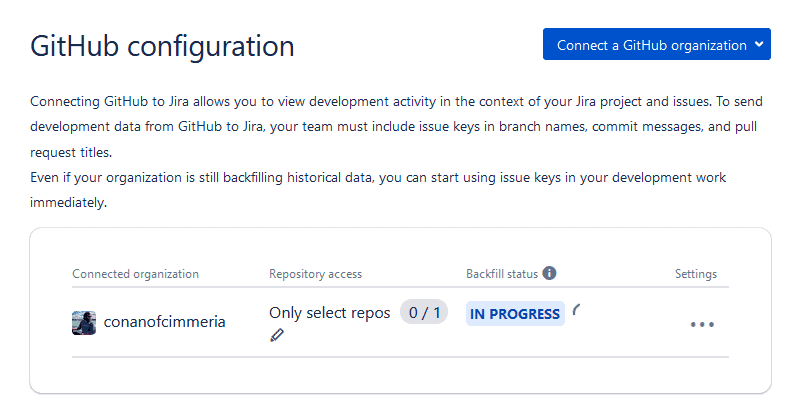
And just like that, you’ve just set up your GitHub integration with Jira. The GitHub for Jira app will start picking up your GitHub data and sending it over to your Jira projects — that’s what the blue In Progress tag means. Once that’s done, you’ll see that data in your Jira issues!
Anyone working in your Jira projects can use a GitHub issue number to link it with a Jira issue, and see branches, commits, and pull requests without leaving Jira.
Limitations of this method
So while you can easily set up a GitHub integration with Jira using this free app, is it the best for the job? Here’s why that might not be the case.
- It’s a snapshot: While this integration is easy to set up, it doesn’t give you a full picture of what’s happening in GitHub. That’s fine for some workflows, but some teams need more.
- It’s not a true two-way sync: A two-way sync doesn’t just push data, it also keeps everything up to date in both tools. While you’ll get up-to-date data about what’s going on in GitHub in your Jira projects, your developers won’t have the same level of information.
- It only works for Jira and GitHub: If your organization only uses Jira and GitHub, then this won’t be an issue. But if you have other teams using their own PM tools, spreadsheets, or any other kind of tool, then you’ll need a different integration for each tool.
With this in mind, let’s look at a better way to set up a GitHub integration with Jira that you can rely on.
Second method: Integrate GitHub repositories with Jira using Unito
Unito is a no-code workflow management solution with some of the deepest integrations for the most popular tools on the market, including ServiceNow, Azure DevOps, GitHub, Jira, GitLab, Asana, Trello, Google Sheets, Excel, and more. With a single Unito flow, you can automatically push data from GitHub issues to Jira — and back — keeping everything in sync in both tools. That means developers can keep working in GitHub without hopping into Jira, trusting Unito to keep PMs and team leads in the know automatically.
Here’s why Unito is the best solution for setting up a GitHub integration with Jira.
- It syncs more fields: Whether you need your developers to know which Jira sprint their work is part of or your PMs to get access to GitHub labels, Unito is the best way to sync all your data.
- It’s a true two-way sync: Unito doesn’t just push data from one tool to the other. It keeps everything up to date in real-time, so that everyone’s working with the latest information.
- It works with over 30 tools: Spreadsheets, PM tools, CRM platforms, and databases are just a few examples of all the tools Unito supports.
Step 1: Connect your tools to Unito
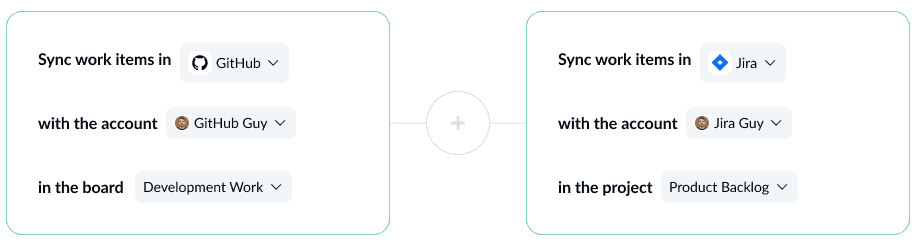
At this stage, you’ll also pick the GitHub repository and Jira project you want to sync.
Step 2: Set flow direction
This will determine where new issues are created. If you’re only looking to dispatch work from Jira to GitHub, for example, set up a one-way flow from Jira to GitHub.
Step 3: Set up rules
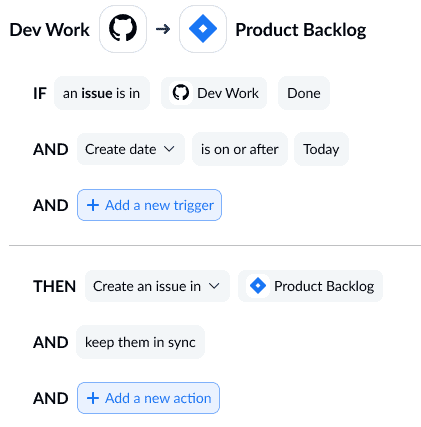
Rules allow you to filter out the issues you don’t want synced. You don’t have to push all issues between tools. Unito can automatically filter out issues based on their type, labels, milestone, sprint, and more.
Step 4: Map fields
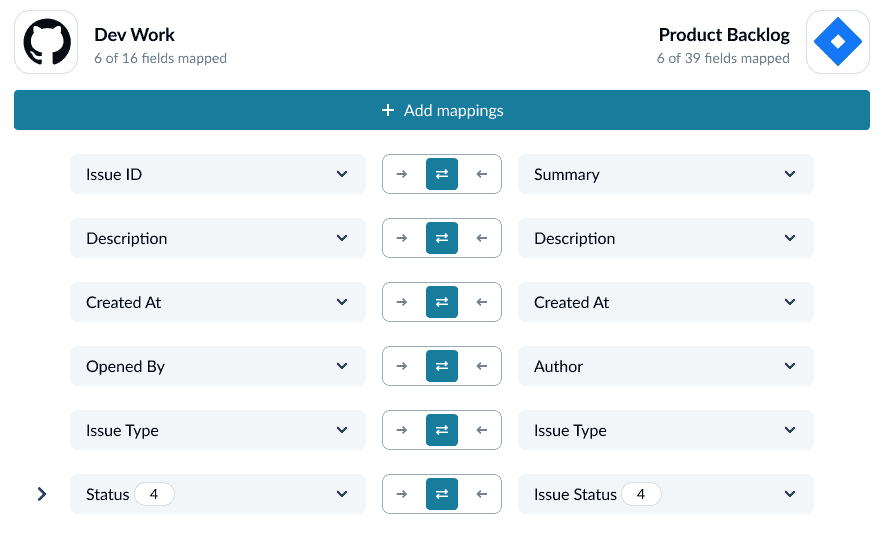
Field mappings tell Unito how data needs to move between tools. Unito can map most of these automatically, but it’s a good idea to review these mappings and tinker with them as needed.
And that’s it! Now just launch your flow and watch as your GitHub integration with Jira automatically pushes issues between tools, keeping everything in sync.
Ready to integrate Jira with GitHub?
Meet with our team to see what this Unito integration can do for you.
FAQ: GitHub-Jira integration
Can GitHub integrate with Jira?
Absolutely! Not only can you integrate GitHub with Jira, but you have a few options to choose from:
- A Jira integration for GitHub built by Atlassian: This app can be added to GitHub repositories and Jira projects without paying a dime. It’ll automatically push data to Jira based on changes happening in GitHub, allowing you to track branches, commits, PRs, and more. It’s the best option for a simple, no-frills integration, though it won’t work for every use case.
- Third-party automation solutions: These platforms allow users to build automations between tools without any technical knowledge. They push data in one direction, based on a pre-determined trigger. You could, for instance, use automation to create an issue in Jira whenever a PR is created in GitHub. But a single automation won’t do anything beyond one action, meaning you won’t get updates in Jira for changes in GitHub, making these tools limited. Examples of these tools include Zapier and Tray.io.
- Third-party two-way sync solutions: Automation just pushes data. A two-way sync solution creates a relationship between work items in both tools, meaning you’ll get up-to-date data in both as you work. If, for example, you sync a GitHub repository with a Jira project, any GitHub issues you create will get automatically paired with a new Jira issue. Change assignees or add comments in GitHub and you’ll see the same thing happen in Jira. Unito and Jira Scriptrunner are two examples of these tools.
How do I automate Jira with GitHub?
To automate work in Jira and GitHub, you’ll need to use a third-party solution or Atlassian’s custom app. The latter is a bit more limited in functionality, but it’s free. Third-party automation and two-way sync solutions usually involve an additional subscription, but let you automate work between Jira and GitHub more thoroughly.
How do I import issues from GitHub to Jira?
You can export issues from GitHub in a CSV or JSON format, and then import that data manually into Jira. Note, however, that any changes you make in GitHub after this won’t be reflected in Jira. For that, you’d need a third-party automation or two-way sync solution.